January 24, 2005
Mega Ultra Super Duper update
Just basically revamped the homestar mirror. Good god he made a lot of updates...--Update!--
I made it so that of any of the main pages when you hit quotes, you'll be served a random one. Un fortunately I haven't been able to get his properly working in IE (as far as I know it either: a> doesn't work at all in IE or b> serves the same quote everytime), but it works fantastically in firefox (I don't know about Opera or Netscape). Outside of that, I think I may make a "tips" subdomain for kitkorp. tips.kitkorp.com (which doesn't exist yet) would just have a bunch of random things you can do to improve performance on your computer. Also may have some "common debugging issues" section where I would post about problems I had recently found on other machines and how I solved the issue. A quick exampleof something that would go on tips.kitkorp.com would be something like this:
Secrets of Firefox 1.0
By Brian Livingston
It's not so long ago that we learned to master the Windows Registry, a buzzing hive of little-known configuration settings. Now we find that Firefox 1.0, the hot new browser released on Nov. 9 by the Mozilla Foundation, has its own hidden playground for us to tweak.
In case you haven't heard, Firefox is rapidly gaining steam as a free replacement for Microsoft's own Internet Explorer browser. OneStat.com, which measures Web behavior in 100 countries around the world, reported on Nov. 22 that IE had lost 5 percentage points of market share in the past six months, dropping to 89% of browser users. Firefox and its predecessor, Mozilla, are up to 7.35% of users. The foundation says 7.5 million people downloaded Firefox 1.0 in the month of November.
That doesn't tell the whole story, though. Experienced Windows admins, who often set the tone for other users, seem to be adopting Firefox at a much higher rate. More than 25% of the visitors to my specialized Web sites — WindowsSecrets.com, BriansBuzz.com, BrianLivingston.com, and the like — are now using some version of Firefox or Mozilla, according to my server logs. That's up from only 10.9% as recently as January 2004.
With all this momentum, it's fascinating to find that many powerful capabilities of Firefox 1.0 are still difficult to find and little known. For example, typing the following strings into Firefox's Address Bar (which the new browser calls the Location Bar) and pressing Enter brings up a wide variety of novel applets:
-
about: shows info on Firefox's version number, copyright, etc.;
-
about:config reveals the Configuration Console, a repository brimming
over with scores of customizable settings;
-
about:cache displays a summary of both your memory and file cache,
with a link to full file listings;
-
about:buildconfig lists the compiler options that were used to create
your version of Firefox (and, since it's open source, anyone can compile a
customized version);
-
about:plugins enumerates your installed add-ons, which can be quite
numerous since Firefox is designed to be modular and extensible; and
-
about:credits is an "Easter egg" that includes the names of hundreds
of developers and testers who worked on the product.
What about:config is and isn't good for
Typing about:config into the Address Bar reveals an enormous list of settings and options (see image, below). This includes everything from the "browser" section, which controls user-interface preferences, to the "network" section, which establishes parameters for connecting to the Internet and other resources.
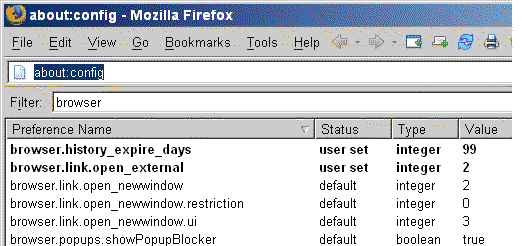
The organization of about:config — let's face it — is a mess. There are settings in here that are left over from the old Mozilla browser suite, which do nothing in Firefox but haven't been removed. Other settings are easily changed through Firefox's visible menus, so there's no good reason to tweak them in the unforgiving about:config environment.
That leaves a number of settings that can really make a big difference in your enjoyment of Firefox as a browser. With a few simple precautions, explained below, you can try different configurations with little risk.
The care and feeding of about:config
There are three ways to edit the settings in Firefox's Configuration Console:
1. Direct editing. In the Firefox window, you simply right-click any row, which brings up a context menu. On that menu, you click Modify to change a value, New to create a new value, or Reset to restore a value to its default. A setting looks like this:
browser.history_expire_days user set integer 99
2. Editing User.js. You can also insert lines into a file named User.js. Firefox reads this file and adopts any settings it finds there. The file does not exist by default and must be created, if desired.
The file uses a different format to specify preferences. The "history expire days" setting shown above would look as follows in User.js:
user_pref("browser.history_expire_days", 99);
Because direct editing in the Configuration Console is so easy, it usually isn't necessary to write lines of code into User.js. Creating such a file, however, can be useful if you wish to override Firefox's defaults on several PCs. (In that case, simply copy the file to the correct location on those machines.)
3. Editing Prefs.js. This file is automatically generated by Firefox when you make changes thorugh its menus or the Configuration Console. It's unwise to edit this file directly, and Prefs.js is mentioned here only for completeness and to advise you against editing it manually.
The files mentioned above — as well as two other customization files, userChrome.css and userContent.css — are located in different folders under Windows 2000/XP and Windows 95/98/Me. This is explained in articles at Mozilla.org, the site of the Mozilla Foundation, and The Edmeister, a private Firefox info site.
You can edit these files without having to find their specific location by using a free, third-party utility called ChromEdit.xpi. After you install this extension and restart Firefox, a new Edit User Files item shows up on the Tools menu.
An excellent tutorial on editing within the Configuration Console is provided by Mozillazine.org, a tips site.
How to backup and restore these crucial files
You can make mistakes when editing configuration files that would prevent Firefox from working properly or even starting at all. For this reason, you should always back up these files before making changes. Everyone will tell you that, but I'm also going to show you how to do it and, more importantly, how to recover in case you make a serious error.
1. Backup your config files. Your customization files are stored in a folder named Profiles on your hard drive underneath username \ Application Data \ Mozilla \ Firefox. To find the different locations for this folder on Windows NT, 2000, XP, 9x, and Me, check the convenient chart at Mozilla.org. Before making edits, copy the Profiles folder to a backup disk or another safe location.
2. How to recover from errors. If your changes make Firefox unstable, close all instances of Firefox and then copy your preferences files from your backup location to the default location and restart Firefox. In extreme cases, when Firefox won't even start, you can rename the User.js file and/or the Prefs.js file to a temporary name and then start Firefox. The browser will revert to a default configuration, allowing you to transfer your "safe" preferences into a new file.
The tweaks you'll want to make right now
Now that you have the basics, we get to the good part: making changes to improve Firefox's performance and capabilities.
Fix a memory leak in Firefox 1.0
Firefox is supposed to dynamically release memory from its RAM cache to other Windows applications as needed. Unfortunately, Firefox 1.0 seems to consume more memory than it should, which hurts performance, when set to the default of 51200 KB (51 MB).
To solve this, Firefox power users recommend limiting the memory cache using the Configuration Console. This frees up memory for other apps, speeding up everything to a greater or a lesser extent, depending on your machine and the applications you run. Here's how the trick works:
Step 1. Type about:config into Firefox's Address Bar and press Enter.
Step 2. Right-click any row, then click New, Integer. Type or paste the following preference name into the dialog box that appears (this is a hidden preference that doesn't exist in the Configuration Console until you create it):
browser.cache.memory.capacity
Step 3. Click OK, then enter the following integer number into the next dialog box, representing 16 MB of RAM for the cache:
16000
Step 4. Click OK to close the dialog box, then close all instances of Firefox and restart it.
For a lengthy discussion of this option, see Mozillazine's forum topic 172041.
Move the disk cache to a faster or larger location
Many Windows users like to locate their disk cache files on a separate hard drive from Windows. This can improve the performance of Windows or whatever program is using the cache, or it can free up space on a primary partition. (The disk cache should not be confused with the RAM cache described above.)
To move Firefox's disk cache, use about:config to create a new preference. (This is another hidden preference that doesn't appear until you create it.)
Type browser.cache.disk.parent_directory into the dialog box that appears, then click OK. In the Value dialog box, enter c:\folder, providing the foldername in which you wish the file to be located.
This and other networking and cache settings are sparely documented by a Firefox developer called Ben C. on his NetPrefs page.
Force frames to be resizable on Web pages
If you visit Web sites that divide their pages into rectangular frames, but some of the frames aren't wide enough for you to see all of the words, you can tell Firefox to put borders around all frames so they're resizable.
To do this, use about:config to change layout.frames.force_resizability from "false" to "true."
Other preference settings
There are literally hundreds of possible preference settings that are accessible via about:config. Unfortunately, there's nothing in the help text that comes with Firefox 1.0 on these settings. A variety of user sites have sprung up to expound on these preferences, but their coverage is spotty and not completely trustworthy.
The best all-around explanation of most Firefox settings has been posted by a developer called GuruJ on his Documented Preferences page. This page also links to a Firefox extension named Preferential, currently in version 0.6.1a. This utility adds an Advanced Preferences item to Firefox's Edit menu, giving you a user interface to a vast array of settings that otherwise would require hand-editing.
Even the "Documented Preferences" page has many holes, which I hope the Mozilla Foundation will quickly and publicly fill in. For example, GuruJ's page describes many settings with a question mark, indicating that the true meaning of an item is unclear. This includes the "frames force resizability" setting I described above. (I had to determine the official stand on this option by contacting Ben Goodger, the foundation's lead Firefox engineer.)
Tweaks for the ultimate in performance
There are several settings and options that can make Firefox run as a much faster browser. You should test these techniques before you roll them out to, say, a thousand workstations in your company.
Speeding up the maximizing of Firefox
By default, when you minimize Firefox, it gives back to Windows most of the RAM the browser was using. It sometimes can take several seconds for the browser window to become fully loaded when you restore the window to its original size. This is one of those "version 1.0" things, in my opinion, that will become more streamlined in future bump revs of the program.
Fortunately, there's a hidden setting that can accomplish the restoration of Firefox windows much more quickly:
Step 1. Use about:config to create a new, Boolean value. Type or paste the following string into the dialog box that appears:
config.trim_on_minimize
Step 2. Click OK to close the dialog box. Change the value from "true" to "false" and restart Firefox.
This doesn't piggishly retain all of the RAM that Firefox has claimed. If Windows needs more RAM to devote to another application, Windows can take it. What the setting does is prevent Firefox from giving up most of its RAM until the memory is actually required elsewhere.
Setting this item to "false" may noticeably slow down other applications while Firefox is minimized, if your PC has less than 256 MB of RAM. If so, change the setting back to "true."
There's an extremely long discussion about the development of this trick, going back to March 2004 (and continuing up through today), in Bugzilla bug report #76831. If you're determined to delve into this, I'd recommend starting with comment 329.
Speeding up Firefox on Windows XP
You can speed up the loading of Firefox on Windows XP by adding it to the programs that XP "prefetches."
To do this, right-click the Start Menu item for Firefox, or any icon you use to start Firefox, and open the Properties dialog box. Add a space plus /Prefetch:1 to the command line and click OK. The resulting line might look as follows:
"C:\Program Files\Mozilla Firefox\firefox.exe" /Prefetch:1
A detailed explanation of XP's prefetch feature is provided by TechRepublic.
Use a "Moox" build that's customized for your CPU
A developer who goes by the name of Moox has compiled the Firefox code into separate executables, optimized for the instruction sets of different CPUs. This provides the biggest performance boost that I've seen (and also consider to be reliable). The developer's PDF white paper on the topic shows reductions of as much as 30% in the time required for Firefox to perform various tasks.
At this writing, there are three separate builds: one for Pentium 4 and AMD Opteron (and other CPUs), one for Pentium 3 and AMD Athlon MP, and one for Pentium 2 and AMD Athlon. The builds are free, of course.
To download the builds, see Moox's Mozilla page.
The big kahuna: fast rendering of Web pages
The most sought-after performance improvements in any browser will always involve how quickly it downloads and renders Web pages. The good news is that Firefox (which is already pretty fast in its default configuration) includes numerous about:config settings that can improve the downloading and display of content. The bad news is that the optimum settings will differ from machine to machine, and there's no consensus on what they should be.
After extensive research, I haven't found a utility or even a well-tested explanation that can guarantee the optimum settings for any particular Windows scenario (Windows 2000 vs. XP, DSL vs. T1, etc.).
There are scores of Web sites that speculate on configuration settings that are said to speed up the browsing experience in Firefox. But these sites largely don't show that they've done adequate testing of the alternatives, much less explain how such tests might have been conducted.
One long discussion post, by a German power user who goes by the name of Laszlo, lists in Mozillazine numerous settings in the content, network, and nglayout sections of the Configuration Console. His post is followed by literally hundreds of comments on various tweaks. I don't feel there's a solid answer here yet.
Another stab at this issue has been undertaken by a poster who goes by the name of Achilles. He proposes four different configuration suites in his Firefox Tweak Guide, depending upon whether you have a slower or faster PC and a slower or faster Internet connection. Again, no testing details or benchmark figures are provided.
At this point, the optimum settings for Web browsing under various configurations must be considered a subject for further study. Firefox is plenty speedy as it is. My recommendation? Download Firefox and enjoy it with the improvements I've described above. I'll give you an update when something truly definitive comes out about this.
Other resources
I haven't even touched in this article on several free, third-party extensions to Firefox that I believe are great enhancements. For a description, see my Nov. 23 Datamation column on Getting the Most Out of Firefox.
Finally, an excellent resource on Firefox annoyances and fixes is Michael Horowitz's always-entertaining Web site, ComputerGripes.com. His site features several pages on Firefox behaviors, good and bad, many of which have been fixed with the release of version 1.0 gold. He also criticizes several other Web sites that need programming improvements to work well with Firefox.
That's it for now. To send us more information about Firefox configuration settings, or to send us a tip on any other subject, visit WindowsSecrets.com/contact. You'll receive a gift certificate for a book, CD, or DVD of your choice if you send us a comment that we print.
Posted by Kickmyassman at January 24, 2005 01:48 PM
Comments
Cool website! And this specific entry looks extremely useful: I'll try applying the various tweaks and changes later, when I have more time to waste. =) If you'd like me to inform you of the results, let me know via e-mail. (I did't want to write it in this comment, cause I hatehatehate spambots, but you already have my e-mail anyway, so it doesn't matter.)
Posted by: David Baumgold at January 25, 2005 06:17 PMPost a comment